In the dynamic realm of finance, the intersection of technology and strategic decision-making has long been a focal point for innovation. With the advent of Artificial Intelligence (AI), financial institutions have found themselves at the precipice of a transformative era, particularly in the domain of Mergers and Acquisitions (M&A). This article delves into the intricate landscape of AI integration within financial institutions, with a keen focus on its tangible progress within the M&A sector.
use of ai by financial insitutions
The use of artificial intelligence (AI) in the financial sector is rapidly increasing, revolutionizing the industry. By innovating processes, AI is changing how firms interact with clients, and make important business decisions. The main drive behind this technology revolution is AI’s ability to automate difficult jobs. AI analyzes huge amounts of data, and offers new insights in speeds that were previously unattainable. The adoption of AI technology into financial institutions is showing to have a huge impact on their overall performance and customer satisfaction rates, improving efficiency, reducing operating costs, and providing individualized client services.
One of the largest banks in the world, JP Morgan, has implemented AI in a very noteworthy way. The bank has been leading the wave of AI use, and can be recognized especially in automating the loan funding procedure. JP Morgan has been able to successfully streamline the loan approval process through the use of machine learning algorithms and data analytics. By reducing wait times, this not only improves the client experience but also increases the accuracy of risk assessment, allowing the bank to make better lending decisions.
Similar to JP Morgan, other financial companies are also making use of AI to transform many stages of their business processes. Wealth management companies, for instance, are utilizing AI to provide individualized investment advice by assessing the market and specific customer characteristics to suggest tailored investment plans. This is best demonstrated by Charles Schwab’s Schwab Intelligent Portfolios, an American investment firm which provides individualized investment advice by using algorithms to assess clients’ objectives and market conditions to create tailored portfolios. Their investment methods are optimized by this AI-driven method, which ensures they meet personal financial goals.
Insurance firms are also introducing AI-powered technologies to handle claims, using data analytics and picture recognition to evaluate damage and perform the claims process quickly and precisely. Lemonade, an American insurance company, uses AI in the insurance industry to accelerate the processing of claims, most notably through its chatbot AI Jim, which can evaluate claims and identify fraud quickly by using machine learning and image recognition, allowing it to approve simple claims in a matter of seconds. Because of Jim, the procedure of filing insurance claims is now much more accurate and efficient.
the actual progress of ai integration in M&A
In the ever-evolving landscape of mergers and acquisitions (M&A), companies are increasingly turning to innovative technologies to enhance their capabilities and streamline processes. According to insights obtained from Bain & Company’s “Global M&A Report 2024,” based on interviews with 300 professionals entrenched in the M&A sphere, a significant trend emerges: the growing reliance on generative artificial intelligence (AI) to bolster M&A strategies.
Currently, 16% of respondents are actively deploying generative AI, with an additional 16% of non-users poised to adopt this technology within the next 12 months. Remarkably, an overwhelming 80% of respondents anticipate integrating generative AI into their operations within the next three years. These adopters are often larger enterprises engaged in moderate M&A activity, averaging three to five deals annually.
Generative AI currently plays a pivotal role primarily in idea generation during sourcing and data review processes. As one respondent elucidated, “Generative AI in the screening process can pick up targets that would not be identified with traditional tools.” Its utility extends to analyzing vast volumes of data during diligence phases, where missing critical information could result in significant losses. By training generative AI to analyze material contracts and identify deviations from model contracts, valuable time is saved, allowing teams to focus on critical areas.

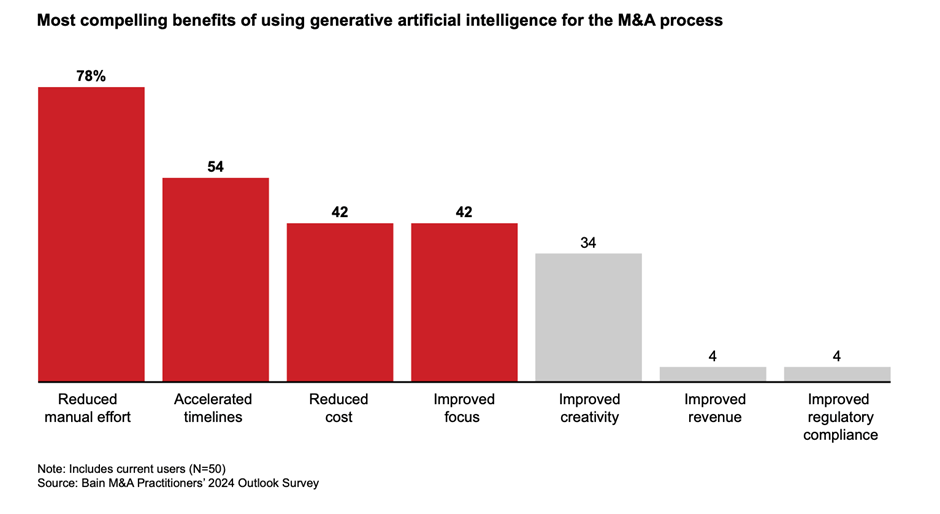
The benefits derived from employing generative AI in M&A are substantial, as reported by 78% of surveyed individuals who experienced productivity gains through reduced manual efforts. Additionally, 54% witnessed accelerated timelines, while 42% reported reduced costs and enhanced focus. Impressively, 85% of early adopters attest that generative AI either met or surpassed their expectations.
Nevertheless, alongside the promise of enhanced efficiency and effectiveness come notable concerns. Among the surveyed professionals, the most prominent risks associated with generative AI implementation include data inaccuracy, privacy breaches, and cybersecurity vulnerabilities.
In summary, the integration of generative AI stands as a pivotal advancement in M&A practices, offering unprecedented capabilities in data analysis, idea generation, and process optimization. While accompanied by inherent risks, the overwhelmingly positive feedback from early adopters underscores its potential to reshape and revolutionize M&A strategies in the coming years.
The Impact of AI on the M&A Process
The introduction of this cutting-edge technology is going to reshape different processes of a corporate activity due to its high potential related to improving productivity and precision, in particular with repetitive tasks, allowing cutting costs by automating tasks, analysing data and making decisions.
In the case of Merger and Acquisitions, the role of AI will most likely modify the data-driven tasks required, such as the target company identification, due diligence and negotiation, while in other cases where human judgment and interpersonal skills are required, AI would only act as a support for the managers and investment bankers.
We will now analyze how AI may impact and transform the M&A process regarding:
- Target company identification
- Due diligence
- Valuation and Pricing
- Post-merger integration
I. Target company identification
AI may have a pivotal role in understanding market trends by analyzing competitors and different strategies a company may want to use by considering all the historical deal outcomes. The introduction of AI in this first step improves the amount of data an investment bank could analyze, by using personalized algorithms which can detect high-potential acquisition targets by analyzing different factors such as financial stability, market competitiveness and growth opportunities.
This process can also be transformed into a continuous screening of the market, evaluating each company not only based on its financial status and market position but by also considering the macroeconomic landscape. This would help to understand if the timing is opportune for an acquisition, taking into account market fluctuations and economic forecasts.
II. Due Diligence
Also in the due diligence phase, where data analysis is crucial, AI will emerge as a powerful ally, by helping analysts to identify potential problems and inconsistencies in the data available.
From the buy-side perspective, the AI could be used for examining public sources searching for ongoing tax and legal disputes, financial reports and media coverage, to guide the management interviews and the information request list in a second phase.
Once the virtual data room is uploaded, AI may help to summarize documents or identify potential risks related to a series of operations done by the counterpart. This would permit the management to focus on the most crucial and essential documents without overlooking the less important ones, which, without the assistance of AI would hardly have been taken into account while doing the analysis, particularly in the case of complex VDRs for larger transactions.
From the sell-side perspective, the VDR can be automatically organized by AI algorithms, making the uploading process substantially more efficient and less time-consuming, while at the same time checking for sensitive information that the vendor should not disclose.
III. Valuation and pricing
The valuation part is fundamental for setting the idea of an initial purchase or selling price and involves understanding the market value of a company. AI can also rewrite this process since usually it is considered a complex and subjective task, while AI would use a data-driven approach.
In this case, AI is capable of fully addressing a wider range of factors and market dynamics compared to traditional valuation methodologies: through the examination of historical financial data, market trends, and competitive landscape, AI can produce more precise and adaptive valuation. This would be particularly efficient for dynamic market sectors characterized by a rapid evolution.
Another way AI can be used is by looking beyond historical analysis, using its potential to simulate different scenarios understanding what would be the possible implications after an acquisition. The power of AI can, for example, be used for making different assumptions on growth rates, cost structure, macroeconomic scenarios and market conditions. This would also facilitate updating the valuation in the event of an abrupt change in market conditions.
Furthermore, traditionally, the valuation was based only on financial metrics, such as revenues or cash flow, without a deep analysis of non-financial data. By introducing AI, there is the possibility of getting a more comprehensive view of the real company value, by analyzing every aspect of a target to make more informed decisions about an acquisition.
IV. Post-merger integration
After having closed a deal, successful post-merger integration is crucial for realizing the full potential of a deal. Since integrating two different companies can be complicated and challenging, AI assists management in identifying shared areas of interest between the companies and aligning their potentially disparate cultures.
AI algorithms have the capability to anticipate potential integration hurdles by examining data from previous mergers, such as employee turnover rates, cultural alignment, and synergy achievement. This approach allows for improved preparation and the development of customized integration strategies. Moreover, AI’s versatility allows for the identification of synergies across various aspects of the acquisition process, ranging from production processes to marketing strategies, often not recognized by the management, effectively maximizing the potential benefits of the merger
Risk and limitation
As we consider the role of AI in M&A transactions, it’s important to recognize the potential risks and limitations associated with this technology. While AI holds immense promise in enhancing efficiency, uncovering valuable insights, and streamlining decision-making processes, it is not without its challenges. Understanding and navigating these risks is essential for businesses to effectively leverage AI while mitigating potential drawbacks that could impact the integrity and success of M&A transactions.
Inaccuracy risk
One significant challenge businesses face when implementing AI solutions is the risk associated with accuracy. While AI technology holds the promise of automating tasks and processes with unprecedented speed and efficiency, inaccuracies can undermine its effectiveness and reliability. The difficulty in verifying whether AI has worked correctly further compounds this issue.
In many cases verifying the accuracy of AI-generated results requires significant time and effort. This raises questions about the true value proposition of AI implementation. Even if a business invests resources in verifying the accuracy of AI outputs, the time spent doing so may outweigh the benefits gained from automation.
Ultimately, the efficacy of AI in business hinges on its ability to deliver accurate and reliable results consistently. Businesses must carefully assess the trade-offs between automation and the need for human oversight to ensure accuracy. Thus, while AI offers tremendous potential, businesses must navigate these challenges thoughtfully to maximize its benefits effectively.
Confidentiality risks
As businesses increasingly rely on AI tools to streamline processes and derive insights from vast datasets, questions arise about the security and confidentiality of sensitive information.
Businesses must grapple with the dilemma of entrusting AI tools with confidential and private documents. While AI has the potential to extract valuable insights from data, there is a legitimate fear of data breaches and unauthorized access to sensitive information. The consequences of such breaches can be severe, ranging from financial losses to damage to reputation and legal liabilities.
To address these concerns, businesses must carefully evaluate the trustworthiness of AI tools and the security measures in place to protect data privacy. This includes conducting thorough due diligence on AI providers, assessing their data security protocols, and implementing robust encryption and access controls.
Furthermore, businesses should prioritize transparency and accountability in their AI practices, ensuring that employees and stakeholders understand how AI tools are being used and how data privacy is safeguarded
Biases
AI algorithms, if not carefully designed and monitored, can perpetuate and even amplify biases present in the data they are trained on. This poses a serious concern, particularly in domains where objectivity and impartiality are paramount, such as M&A transactions.
In the context of M&A, where decisions can have far-reaching implications for stakeholders, maintaining objectivity and fairness in the analysis is crucial. However, if AI systems inadvertently incorporate biases from historical data or societal prejudices, it can lead to discriminatory and not ideal outcomes.
For example, AI algorithms may inadvertently favor certain types of companies or overlook potential targets based on biased assumptions about industry norms or past performance. This can undermine the integrity of the M&A process and result in suboptimal decision-making.
The AI Investment Game: Big Tech’s Strategy to Bankroll Growth and Disrupt VC Markets
Building on how AI impacts processes within Financial Institutions, the second part of the article will focus on the Tech Industry.
Artificial Intelligence is undoubtedly one of the most disruptive revolutions in technology, and no wonder giants like Amazon, Google, Microsoft and Apple want to keep up with it. In the following sections, by analyzing trends, we will understand and prove how big techs are fostering inorganic growth through acquisition of AI startups.
According to CNBC’s TechCheck, big techs could be using AI investments to bankroll themselves. During the past years Microsoft and Google have poured billions into the biggest names in the AI startup world, effectively replacing what used to be the role of high-profile, highly capitalized tech investors like Tiger Global and Softbank.
The reason behind that is dual:
- First, acquisition of high-tech startups allow big companies that rely on innovation to grow inorganically without massive R&D spending and potential sunk costs (given the rapid pace of technological evolution)
- Second, many of those startups guarantee – by the stipulation of particular contracts – that their Large Language models will be trained exclusively on the cloud of the buyer. This way, startups get a favorable price on one of the most important infrastructure of the company, but entities like Microsoft, Google and Amazon see their cloud revenues massively increased. Suffice it to consider that that for Amazon, its cloud division represents 14% of the revenue, while for Google and Microsoft, it’s respectively 10% and 40%.
Big tech’s cloud units have great marginality (for example Amazon’s AWS has more than 30% marginality), and so the circle begins: in essence, big tech’s profits are used to invest in AI startups, and that comes back in form of cloud revenues, thanks to the above-mentioned marginality. It is no coincidence that OpenAi trains its model on Azure, and Anthropic uses AWS and Amazon’s chips.
The most immediate consequence of that is the shake given to the Venture Capital world. In fact, big techs are more than willing to buy startups at a much higher valuation: at the end, they will benefit no matter what. Moreover, VC investing is crowd out for other two reasons:
- To invest in an AI startup you have to put hundreds of millions of dollars but VC funds try to buy at a low valuation trying to maximise their return – as that is their only source of revenue
- Big techs offer a great benefit that funds cannot: they give access to expensive GPU chips through their cloud service. Note that this also pushes up the valuation of the startup, as the value of the assets goes immediately up
Other noteworthy Trends
- In terms of activity escalation, Nvidia stands out, significantly increasing its engagement from supporting 5 AI startups in 2022 to 32 in 2023, solidifying its position within the generative AI landscape.
- Both Apple and Meta, historically less active in investments and lacking venture arms, did not publicly disclose any AI startup investments in 2023, setting them apart from other tech giants in this regard.
- Given the resource-intensive nature of AI development, startups are forging partnerships with major tech players such as Google, Microsoft, Amazon, and Nvidia to gain access to their cloud infrastructure, chip technology, and financial resources. Consequently, these collaborations are also bolstering competition among these tech giants in the cloud computing and chip markets.
Challenges Posed by Tech Conglomerates’ AI Acquisitions
The trajectory of acquisitions by major tech conglomerates within the AI startup sphere presents profound risks that warrant scrutiny. Foremost, it engenders heightened competition for talent and resources, pitting nascent startups against formidable incumbents armed with considerable financial and technological might. This unequal playing field not only jeopardizes the prospects of emerging ventures but also consolidates power within a select few, potentially stifling diversity and innovation within the industry.
The rampant acquisition spree perpetuated by tech giants threatens to homogenize the AI landscape. When startups are assimilated into larger corporate entities, their distinct ideas and methodologies may be subsumed, leading to a standardization of AI technologies and solutions. This prospect undermines the dynamism and creativity inherent in a diverse ecosystem of AI innovators.
Moreover, the monopolistic tendencies observed in the current market trajectory pose grave risks to the democratization of AI. By concentrating essential resources and expertise within a handful of corporations, particularly in data and computing power, smaller players such as researchers and medium-sized enterprises face the specter of overreliance on Big Tech. This dependence not only hampers access to cutting-edge innovations but also fosters a cycle of technological dependency that undermines the broader democratization and accessibility of AI advancements.
In essence, the unchecked consolidation of power and resources within the AI sector poses existential risks to both the competitiveness and democratization of AI innovation. Addressing these risks necessitates a concerted effort to foster a more equitable and diverse ecosystem that empowers a multitude of stakeholders to contribute to and benefit from the transformative potential of AI technology.
A glimpse into the future
Healthcare and Industrials Lead AI M&A Activity
Looking ahead, the outlook for sectors leading M&A activity in AI is marked by significant trends and investments. Among these, healthcare and industrials stand out as primary targets for big tech’s vertical AI investments. In 2023, Nvidia notably supported eight AI startups in healthcare and life sciences, with a particular focus on AI-driven drug discovery, underscoring the chipmaker’s commitment to this sector. Concurrently, the industrial landscape is witnessing a surge in AI-driven innovations aimed at automating operations. Big tech companies are directing their attention towards applications in materials development, manufacturing, and warehousing, recognizing the potential for efficiency gains through automation. For instance, Amazon’s Industrial Innovation Fund recently invested in Veo Robotics, a startup specializing in AI-powered robotics safety, highlighting the growing interest in this area. Similarly, Microsoft’s M12 and NVentures recently backed Figure, a humanoid robotics startup, with a significant Series B investment of $675 million, signaling a burgeoning interest in robotics technology. These developments indicate a shifting landscape where healthcare and industrials emerge as focal points for M&A activity in the AI sector, driven by the quest for innovation and efficiency gains.
The Role of AI in M&A Resurgence
Despite a downward trend in overall big tech acquisition activity, the landscape could undergo a reversal with the rise of AI. Traditionally, major tech players have pursued acquisitions to access tech talent and diversify into new markets and product offerings. However, recent data indicates a notable decline in big tech acquisitions, hitting an 18-quarter low in Q2’23. This downturn can be attributed to several factors, including a more stringent regulatory environment, particularly in regions like the US and Europe, where antitrust scrutiny has intensified. Additionally, strategic acquirers have adopted a risk-averse approach, contributing to the decrease in acquisition activity.
Amidst this backdrop, AI stands out as a potential catalyst for rejuvenating M&A activity within the tech industry. While big tech firms may be scaling back on traditional acquisitions, there is a notable uptick in AI investment activity. Microsoft, for instance, has significantly increased its investment in AI companies, backing nine such ventures in 2023, compared to just three in the previous year. Notably, Microsoft’s M12 venture arm has played a pivotal role in this surge, completing five AI deals in the current year alone.
This shift in focus towards AI investments underscores the growing importance of artificial intelligence as a strategic asset for tech giants. As they align their investment strategies with broader corporate objectives, the resurgence of AI-related M&A activity holds the potential to reshape the tech landscape, driving innovation and market expansion in the process.
Authors: Pietro Cundari, Giulia Veggetti, Edoardo Signorelli, Matteo Girardi, Joao Henriques Martins Vieira, Fredrik Stafford
You must be logged in to post a comment.