INTRODUCTION:
Novo Holdings, the Danish investment company and majority shareholder of Novo Nordisk, has recently been linked to a potential acquisition of Catalent, one of the world’s largest contract manufacturers. Novo Nordisk, currently the world’s second most valuable pharmaceutical company and Europe’s largest by market capitalization, has garnered significant attention due to its market dominance in diabetes and obesity drugs, particularly its blockbuster weight-loss drug, Wegovy.
This potential deal represents a strategic move to enhance pharmaceutical manufacturing capabilities, addressing the soaring demand for Novo Nordisk’s groundbreaking therapeutics. By acquiring Catalent, Novo Holdings aims to expand Novo Nordisk’s production capacity and further solidify its position as a leader in the global healthcare sector. Such a partnership could have transformative implications for the production of advanced therapeutics and the broader pharmaceutical manufacturing landscape.
The transaction would involve the strategic transfer of three Catalent fill-finish sites in Italy, Belgium, and the U.S. to Novo Nordisk for $11 billion post-acquisition. These facilities are slated for exclusive use in producing injection pens, critical for Novo Nordisk’s supply chain. However, the deal is under scrutiny from EU antitrust regulators, who have sought feedback from competitors and customers on potential anti-competitive concerns across the contract development and manufacturing organization (CDMO) industry.
While Novo Holdings anticipates closing the deal by the end of the year, it faces regulatory hurdles, including a preliminary review by the European Commission and ongoing inquiries from the U.S. Federal Trade Commission. As the obesity drug market heats up, with rivals like Eli Lilly introducing competing therapies, this acquisition represents Novo Nordisk’s strategic response to maintain its competitive edge in a sector projected to be worth $150 billion by the early 2030s.
COMPANIES OVERVIEW
Novo Nordisk:
Novo Nordisk A/S, founded in 1923, is a leading global healthcare company headquartered in Bagsværd, Denmark. The company specializes in developing innovative treatments for diabetes and other serious chronic diseases. It operates in two main segments:
- Diabetes and Obesity Care, which includes treatments for diabetes, obesity, cardiovascular conditions, and other related areas.
- Rare Disease, focusing on rare blood disorders, such as hemophilia, and hormone-related conditions.
With a market capitalization exceeding $400 billion as of 2024 and annual revenues surpassing $33.7 billion in 2023, Novo Nordisk has experienced remarkable growth, primarily driven by its cutting-edge diabetes and obesity treatments. As of the end of 2023, Novo Nordisk employed approximately 64,319 people worldwide.
As the most valuable company in Europe, Novo Nordisk not only plays a pivotal role in the pharmaceutical industry but is also a cornerstone of Denmark’s economy. The company is recognized for its extensive research and development efforts, strong global presence, and commitment to addressing the growing burden of chronic diseases worldwide.
Catalent:
Catalent Inc., headquartered in Somerset, New Jersey, is a global leader in drug development, advanced manufacturing, and delivery technologies for pharmaceuticals, biologics, cell and gene therapies, and consumer health products. Founded in 2007 and listed on the New York Stock Exchange in 2014, the company employs approximately 16,900 people worldwide as of 2024.
Catalent operates through four primary business segments:
- Softgel and Oral Technologies: Specializing in advanced oral drug delivery solutions.
- Biologics: Focusing on biologic drug development, large-scale production, and cell and gene therapies.
- Oral and Specialty Delivery: Delivering innovative oral and specialty delivery platforms for complex formulations.
- Clinical Supply Services: Providing supply chain management and logistics for clinical trials.
With revenues of approximately $4.3 billion in 2023, Catalent has decades of experience in addressing complex manufacturing and delivery challenges. The company’s services encompass drug formulation, development, large-scale production, and supply chain management, making it a vital partner for pharmaceutical and biotech firms.
MARKET OVERVIEW
Healthcare M&A have demonstrated resilience and growth in 2024, driven by evolving industry dynamics and the strategic need to adapt to a competitive landscape. Novo Nordisk’s $16.5bn acquisition of Catalent underscores the sector’s strategic shift to secure supply chains and boost production capacity. This focus on consolidation is particularly evident in the glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) space, as seen with Roche’s acquisition of Carmot Therapeutics and Eli Lilly’s purchase of Nexus Pharmaceuticals’ injectable facility earlier this year. These transactions reflect how companies are responding to growing demand for GLP-1 therapies, particularly in diabetes and obesity treatment. While these moves suggest a trend toward internalizing production capabilities, experts caution against viewing this as a widespread shift. Many firms continue to favour asset-light models, leveraging contract manufacturing organizations to maintain flexibility and minimize capital expenditure.
M&A remains a crucial lever for growth as pharmaceutical companies address pipeline gaps and prepare for key patent expirations. With the IPO market remaining tentative, dealmaking offers a reliable avenue for sustaining momentum and driving innovation. The significance of these strategies is evident in data from PwC’s Annual CEO Survey, which found that 54% of health industry leaders plan to pursue acquisitions within the next three years. This underscores the central role of M&A in helping companies stay competitive and adapt to an evolving market.
Quantitative data further highlights the sector’s dynamism. According to Bain & Company, the pharmaceutical and biotech subsector experienced a 73% increase in deal value during the first nine months of 2023, despite a 10% decline in transaction volume. This upward trend has continued into 2024, with projections indicating that deal value will slightly surpass 2023 levels. By mid-2024, private equity buyouts in North America had already exceeded the total for all of 2023, driven by pent-up demand and a willingness to compromise on pricing.
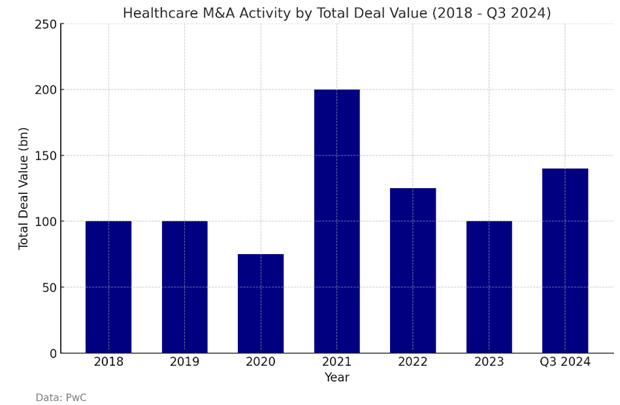
Healthcare services have played a significant role in this resurgence. In the third quarter of 2024, healthcare M&A activity increased, with healthcare services accounting for 42% of this volume. A notable example is TowerBrook and CD&R’s $8.3 billion acquisition of R1 RCM. Globally, the first half of 2024 saw M&A activity valued at $1.0 trillion, marking a 4% increase compared to the same period in the previous year, though still below the ten-year average of $1.5 trillion.
These figures underscore the healthcare sector’s adaptability and sustained appeal to investors, even amid economic and regulatory uncertainties. A strategic focus on acquiring innovative assets and services continues to drive M&A activity, positioning the sector for ongoing growth and transformation in the years ahead.
DEAL RATIONALE:
The acquisition of Catalent by Novo Holdings, the parent company of Novo Nordisk, for $16.5 billion, along with an additional $11 billion investment in three key facilities, would mark one of the largest pharmaceutical deals in recent years. This strategic move is designed to significantly enhance Novo Nordisk’s production capacity for diabetes and obesity treatments, aligning with the rapidly increasing global demand for these therapies.
Central to this acquisition is the need to address the surge in demand for Novo Nordisk’s anti-obesity and antidiabetic medications. The existing production facilities have struggled to keep pace with this growing demand, driven by rising global obesity rates, increased social and medical acceptance of anti-obesity medications, and product innovations like Wegovy and Ozempic, which have redefined the market with their proven clinical effectiveness.
The acquisition of Catalent’s facilities in Anagni, Bloomington, and Brussels offers Novo Nordisk an immediate strategic advantage. These facilities are critical to increasing production capacity and optimizing distribution:
- Anagni Facility: Strategically positioned to serve the European market efficiently.
- Bloomington Facility: A pivotal hub for North American distribution, the company’s fastest-growing market.
- Brussels Facility: A global logistics hub supporting both production and intercontinental distribution.
Together, these facilities are projected to boost Novo Nordisk’s production capacity by 35% over the next two years, while also reducing supply chain delays. Biologic drugs like Ozempic require highly complex manufacturing processes and advanced infrastructure. By internalizing these capabilities, Novo Nordisk can respond more effectively to demand fluctuations and reduce reliance on external suppliers.
However, this ambitious strategy is not without risks. The potential for excess capacity looms if demand for Wegovy and Ozempic stabilizes or declines due to increased competition, regulatory changes, or unforeseen side effects. Additionally, integrating Catalent’s three large facilities into the existing production network introduces operational complexities. Differences in processes, standards, and enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems across the sites may pose logistical and managerial challenges, potentially delaying harmonization efforts.
Despite these risks, the acquisition provides notable opportunities for supply chain optimization. By gaining direct control over production, Novo Nordisk can enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and improve logistics. The integration of Catalent’s facilities is expected to achieve significant operational synergies, including:
- Enhanced Production Efficiency: Closed-loop production techniques in the acquired facilities are anticipated to improve net yield by 10% compared to Novo Nordisk’s current standards.
- Cost Reduction: Centralized production and improved logistics are projected to lower operational costs by 10-12%, resulting in annual savings of $400-500 million.
From a financial perspective, the $27.5 billion investment is expected to deliver a net return on investment (ROI) of 15% within five years, surpassing industry benchmarks for comparable deals. Although the acquisition will initially increase Novo Nordisk’s debt, the company’s structured plan to generate incremental cash flows ensures long-term profitability and financial resilience.
Overall, the acquisition of Catalent represents a bold strategic move by Novo Nordisk, aiming to solidify its leadership in the diabetes and obesity treatment market. By addressing immediate production challenges while optimizing supply chain operations, the deal positions the company for sustainable growth and competitive advantage in the years ahead.
Authors: Dragos Filipas, Bruno Montanaro, Leonard Geissinger, Mark-Alexandru Timisan-Matei, Maximilian Lenhard, Razvan-Cristian Gliga.
You must be logged in to post a comment.