Nippon Steel Corp, the Japan based integrated steel manufacturer producing basic shapes, engineered products, chemicals, and advanced materials, is to acquire United States Steel Corp, the United States based steel producer serving automotive, construction, appliance, energy, containers, and packaging industries. The deal is currently pending, as of May 3rd, because of additional requests issued by the Department of Justice and the interest on the target company of Ancelor Mittal, the Luxembourg based steel and mining company.
COMPANIES OVERVIEW
Nippon Steel Corporation (NSC)
Founded in 1950 and headquartered in Tokyo, NSC is Japan’s largest steelmaker and one of the world’s leading steel manufacturers. NSC has a global crude steel production capacity of approximately 66 million tons and employs approximately 100,000 people in the world. NSC established a joint venture in the United States around 40 years ago and has focused on building cooperative and good relationships with employees, labor unions, suppliers, customers, and communities. As the ‘Best Steelmaker with World-Leading Capabilities,’ NSC pursues world-leading technologies and manufacturing capabilities and contributes to society by providing excellent products and services. NSC operates through five different segments:
- Steelmaking and steel fabrication: it’s the core and most profitable business of the company; it produces and distributes steel sheets, plates, bars and wire rods, pipes and tubes, and machinery parts.
- Engineering and Construction: it develops steel plants, heat management facilities, and industrial machinery and equipment.
- Chemicals & Materials: the Chemicals branch deals with chemical products, carbon materials, and epoxy resin products; the Material one, instead, manufactures and trades semiconductors, stainless steel foils, silicon carbide wafers, carbon fibers, and metal substrates for catalytic converters.
- System solutions: includes information technology infrastructure services.

In FY23 NSC has highly increased its price from 2137¥ (2022) to 3123¥, demonstrating strong financial health, with key ratios such as ROE at 18.3% and ROA at 7.8%, both way above their last 5Y historical average.
United States Steel Corporation (U.S. Steel)
Founded in 1901, U. S. Steel is a leading steel manufacturer headquartered in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, with world-class operations across the United States and Central Europe. With an unwavering focus on safety, the Company’s customer-centric Best for All® strategy is advancing a more secure, sustainable future for U. S. Steel and its stakeholders. With a renewed emphasis on innovation, U. S. Steel serves the automotive, construction, appliance, energy, containers, and packaging industries with high-value-added steel products. The Company also maintains competitive advantages in low-cost iron ore production, mini mill steel making, and best-in-class annual raw steelmaking capabilities of 22.4 million net tons.
United States Steel Corp. operates through the following segments:
- North America Flat-Rolled Products: includes managing steel plants and production facilities that manufacture slabs, rounds, strip mill plates, sheets, tin mill, iron ore, pellets, pig iron, and coke.
- Mini Mill: produces hot and cold-rolled, coated sheets and electrical steels.
- U.S. Steel Europe: involves the production and marketing of sells slabs, strip mill plates, sheet, tin mill products, and spiral welded pipe.
- Tubular Products: manufactures and trades seamless and electric resistance welded steel casing and tubing, line pipe, and mechanical tubing.
FY23 United States Steel Corp. performances have further deteriorated last year’s trend, with a 68% decrease in EBIT and a 66% decrease in Net Income compared to FY22. As for ratios, the company had FY23 ROE of 8.42% and ROA of 4.5%, both below the 5Y historical average.

DEAL-SPECIFIC MARKET OVERVIEW
Metal & Steel Processing Analysis
The Global Steel Processing Market had a valuation of $647.7 billion in 2021 and is anticipated to hit $884.1 billion by 2031, with a compounded annual growth rate (CAGR) of 3.1% from 2022 to 2031. Steel processing encompasses a suite of methodologies and procedures aimed at converting raw steel into refined products suitable for diverse industries. This involves employing cutting-edge technologies and machinery to shape, cut, mold, weld, and coat steel according to precise customer specifications. The process of steel processing encompasses multiple stages, including melting, casting, rolling, forging, machining, and coating. Each phase demands specialized equipment and techniques to ensure that the final steel products adhere to requisite standards of strength, durability, and quality.
Market Dynamics
The robust demand for steel within the construction sector stands as a key driver propelling the growth of the steel processing market. Renowned for its strength and durability, steel serves as a cornerstone material in construction endeavors, thus becoming indispensable for a myriad of infrastructure projects. With nations continuing to channel investments into infrastructure enhancements, the trajectory of steel demand within the construction realm is poised for ascent, consequently bolstering the steel processing market. Moreover, escalating population figures coupled with urbanization trends underscore a surge in requisites for both residential and commercial edifices, thereby amplifying the call for steel. Furthermore, advancements in steel processing technologies have yielded heightened efficiencies and cost-effectiveness, rendering it an enticing option for construction enterprises.
The fluctuations in prices of raw materials like iron ore, coal, and scrap metal wield substantial sway over the steel processing market. Oscillations in these prices can reverberate through the cost dynamics of steel production, thereby impacting the profitability margins of steel processing entities. A surge in raw material costs may engender elevated operational expenditures for steel processing firms, potentially translating into diminished profit margins or even losses should they fail to transfer these augmented costs onto their clientele. Conversely, downturns in raw material prices may furnish steel processors with widened profit margins. To cushion against the repercussions of erratic raw material prices, steel processing firms may resort to hedging strategies such as futures contracts to secure fixed prices for raw materials. They may also explore alternate sources of raw materials or endeavor to curtail reliance on singular suppliers, albeit actions that could impede market growth.
The steel processing market teems with a plethora of opportunities beckoning businesses to diversify their product portfolios and penetrate untapped markets. By honing their focus on delivering top-tier steel products tailored to the construction, automotive, or energy sectors, enterprises can capitalize on the burgeoning demand for steel across these domains. Within the construction sphere, steel finds utility across a broad spectrum of applications ranging from erecting bridges and towering skyscrapers to fortifying concrete structures. As the wave of urbanization persists in stoking demand for fresh construction ventures, the clamor for premium-grade steel products is slated for expansion. This scenario not only unfurls avenues for steel processors to innovate and cater to the unique requisites of the construction sector but also beckons as a strategic juncture for businesses to broaden their horizons and fortify their footing for sustained prosperity.

Source: MRFR database and Analyst review
The report profiles key players in the steel processing market, including China Baowu Group, ArcelorMittal, Ansteel Group, Nippon Steel Corporation, Shagang Group, POSCO, HBIS Group, Jianlong Group, Shougang Group, and Tata Steel Group. This market is segmented based on method, steel type, product end-use industry, and region. Methods include blast furnace and electric arc furnace, steel types range from alloy steel to carbon steel, products span flat, long, and tubular steel, while end-use industries encompass building and infrastructure, automotive, metal products, mechanical equipment, transport, electrical equipment, and domestic appliances. Regions analyzed include North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and LAMEA.
The aerospace sector serves as a significant driver for the steel processing market. Steel’s strength, durability, and lightweight properties make it a favored material for aircraft construction, particularly as the aerospace industry seeks more fuel-efficient and eco-friendly solutions. Lightweight materials, including high-strength steel alloys, contribute to fuel efficiency and carbon emission reduction. While steel is employed in various aircraft components, its usage is particularly prominent in critical parts like landing gear, wing elements, and engine components.
However, the steel processing market is heavily influenced by global economic trends. Economic downturns typically lead to reduced spending, thereby dampening demand for steel products across sectors such as construction, automotive, and appliances. The burgeoning demand for customized steel products presents a lucrative opportunity for steel processing companies. By offering tailored solutions that meet specific customer requirements, these firms can differentiate themselves and attract new business. Customization enables the creation of unique solutions tailored to individual needs, fostering operational improvements, efficiency gains, cost savings, and increased profitability.
Among analyzed regions, Asia-Pacific is expected to lead in market revenue by 2031, followed by Europe, North America, and LAMEA. The dominance of Asia-Pacific and Europe is attributed to growing construction demand.
Market trends indicate growing demand from automation and construction industries. Steel’s strength makes it indispensable in construction for building bridges, highways, and residential, and commercial properties, with increasing urbanization further driving demand. The automotive industry also relies heavily on steel due to its welding capabilities, while technological advancements enhance efficiency and cost-effectiveness, expanding opportunities for steel processors.
Technological advancements in manufacturing, along with increased utilization of steel in end-use industries, are projected to boost market growth. However, fluctuations in raw material costs and machinery equipment, coupled with regulatory hurdles, pose challenges to market expansion.
DEAL RATIONALE
The acquisition of US Steel Corp by Nippon Steel Corp is being interpreted by bankers as a reaction to the growing wave of Japanese companies pushing for overseas acquisitions. This new trend comes as a response to their shrinking domestic market and is facilitated by the constraints Chinese groups are now face in buying US corporations. Nippon Steel aims to inject its advanced technologies into U.S. Steel, enhancing product quality, operational efficiency, and decarbonization efforts. In fact, even if both companies manufacture steel sheets for auto makers, Nippon Steel manufactures “high value-added” steel sheets, while US Steel, so far has been producing just regular products.
Financial and Strategic Growth perspective:
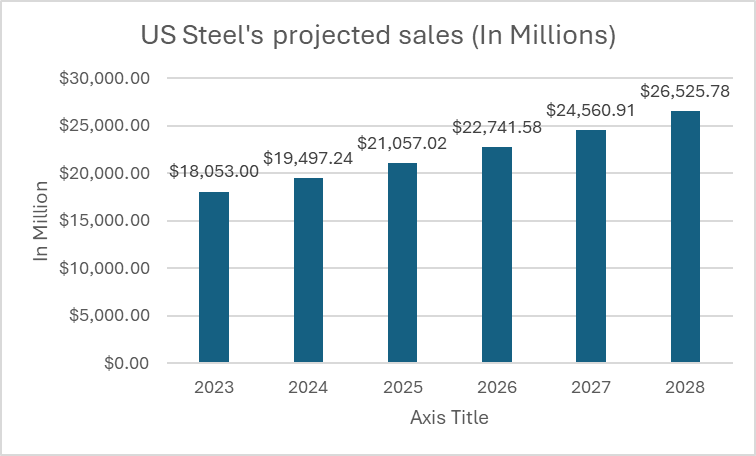
About the financial growth perspective, the acquisition of U.S. Steel is first aimed at fostering the growth of the Japanese steel giant. Growth that has slowed down since the rise of Chinese steel corporations (China is now the biggest producer of steel in the world with a production of 1,019.1 million metric tons in 2023) and an inevitable shrinking of Japanese domestic market. Eiji Hashimoto, President, and CEO of Nippon Steel has underlined the potential for U.S. Steel’s sales to increase by approximately 8% annually over the next five years. This increase is anticipated to have an immediate positive effect on Nippon Steel’s profitability starting from the first fiscal year following the acquisition’s finalization. Considering that U.S. Steel reported revenues of $17.4 billion in 2022, which accounted for about 18% of the combined company’s consolidated net sales, projections suggest that sales could rise to nearly $30 billion by 2030.
Strategic and Financial rationale:
- Common objective on decarbonization goal and technological integration: Nippon Steel and U. S. Steel share the goal to decarbonize by 2050 and recognize that solving sustainability challenges is a fundamental pillar of a steelmaker’s existence and growth. Nippon Steel is developing three breakthrough technologies, which will be shared with U.S. Steel to progress towards its goal of achieving carbon neutrality by 2050, including hydrogen injecting technology into blast furnaces, high-grade steel production in large-size electric arc furnaces, and hydrogen use in direct iron reduction process. Nippon Steel and U. S. Steel will integrate these technologies, including transferring Nippon Steel’s cutting-edge technologies for Electrical Steel (NGO), Automotive Flat Products and others, to maximize synergies and achieve a greener future.
- National Security: Both Japan and the USA are now facing the challenge of competing with the rise of China and India. In the steel production industry, in particular, these two emerging countries represent the first and second player, as of metric tons of steel produced. By bolstering U.S. Steel, the deal is seen to advance American national security interests. In fact, the company, after the acquisition, is prospected to enter the top 3, in the steel production industry.
- Global expansion: combined, the two companies, have a Global crude steel production capacity of 88Mt/Y. It is also to be recognized that the US are the third largest consumer of steel, with a demand of almost 95Mt/Y. Today, the US is self-sufficient only for the 66% in the steel industry, so a better integration with the Japanese company and the right investments, could lead to a larger production to sustain the always rising US demand for crude steel.
DEAL STRUCTURE
The acquisition of United States Steel Corp (U.S. Steel) by Nippon Steel Corporation (NSC) has been a landmark deal with significant implications for the steel industry and beyond. With an enterprise value of USD 14.9 billion, including USD 13.7 billion in equity and USD 1.1 billion in target net debt, the transaction represents a strategic consolidation in the global steel market. NSC, Japan’s largest steelmaker, will acquire a 100% stake in U.S. Steel in an all-cash tender oSer, signifying a crucial expansion in its global footprint and capabilities.
This deal has attracted attention not just for its financial aspects but also for its broader socio-economic and political implications. U.S. Steel, with its deep roots and iconic status in the American manufacturing landscape, has been a symbol of American industrial prowess since its founding in 1901. NSC, meanwhile, has emphasized the transaction’s potential to deliver clear benefits to U.S. Steel, its workforce, the broader steel industry, and American national security. By leveraging NSC’s financial investment and advanced technologies, the aim is to drive greater quality and competitiveness for U.S. steel while reinforcing American supply chains and economic defenses.
Delving into the fiscal details, the transaction is anchored by firm financials and valuation benchmarks that speak to the strengths of both corporations involved. For instance, the deal’s valuation on U.S. Steel was influenced by its solid fundamentals, such as a net income of USD 1,149.00m and a robust cash flow from operations amounting to USD 2,466.00m, as reported on. These figures reflect a company with a stable financial base, capable of generating healthy cash flows. On the flip side, Nippon Steel’s willingness to engage in a full buyout with an all-cash oSer reflects their strategic commitment, as explained directly on U. S. Steel’s website, “NSC to acquire U. S. Steel for $55.00 per share in an all-cash transaction representing 40% premium, providing certain and immediate value to U. S. Steel shareholders” and the financial muscle to facilitate such a sizable transaction. Nippon Steel’s financials, showing a net income of 5.46 billion USD and total assets worth 70.7 billion USD, demonstrate its capacity to absorb U.S. Steel’s operations without jeopardizing its financial stability. The financial prudence and strategic motivations of this acquisition are evident in the alignment of these metrics, which pave the way for a merger that promises to bolster operational eSiciency and industry competitiveness.

Source: Mergermarket
Adding to the financial contours of the deal, U.S. Steel was valued based on multiples that reflect its position within the industry. As of September 2023, the enterprise value to EBITDA (earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization) multiple stood at 6.91x, and the enterprise value to EBIT (earnings before interest and taxes) multiple was at a higher 11.61x, indicating the premium Nippon Steel Corporation was willing to pay for U.S. Steel’s operational profitability. Furthermore, the premiums paid above the stock price were substantial, with a 39.84% premium one day prior to the announcement, escalating to a 60.91% premium one month before the announcement. This indicates a strong conviction in the value that NSC believes it can derive from the acquisition, reflecting the strategic nature of this transaction.
However, the transaction has also stirred a substantial amount of debate and scrutiny. The White House has expressed that the deal deserves ‘serious scrutiny,’ given U.S. Steel’s core role in U.S. steel production, which is critical to national security. Moreover, prominent politicians and union leaders have voiced their concerns, with some opposition noted due to the potential impact on jobs, national security, and local economies.
Amid these concerns, both companies have reaSirmed their commitment to U.S. Steel’s legacy, ensuring that it remains “an iconic American company for generations to come.” They have stated that U.S. Steel will maintain its headquarters in Pittsburgh and that its products will continue to be mined, melted, and made in America.
The deal has been overwhelmingly supported by U.S. Steel’s shareholders, with more than 98% of the shares voted in favor during a special meeting, which is seen as a strong endorsement of the merger’s value proposition. However, endorsement from other parties, including political figures and the United Steelworkers union, has been mixed
Moreover, the proposed acquisition has been viewed strategically as a counter to China’s rising technological capability in the steel sector, with some arguing that the collaboration between the U.S. and Japan could be a significant move in the geopolitical sphere.
In sum, the NSC-U.S. Steel deal is poised to reshape the landscape of the steel industry, while also becoming a focal point for discussions on the intersection of business, labor, and national policy. It’s a complex tableau where the imperatives of global business strategy meet the imperatives of national interests and workers’ rights.
Authors: Emilio Cornejo, Verdant Majmudar, Tommaso Belotti, Tommaso Denaro, Gianfranco Sovrenigo.
Sources: Mergermarket, Financial Times, Nippon Steel, US Steel, Factset, SEC, Yahoo Finance.
You must be logged in to post a comment.